Airborne Precautions Should Be Followed for Which Illness
For most airborne diseases youll need plenty of rest and fluids. Airborne precautions may be needed for germs that are so small they can float.
Airborne precautions are designed to interrupt the airborne transmission route.
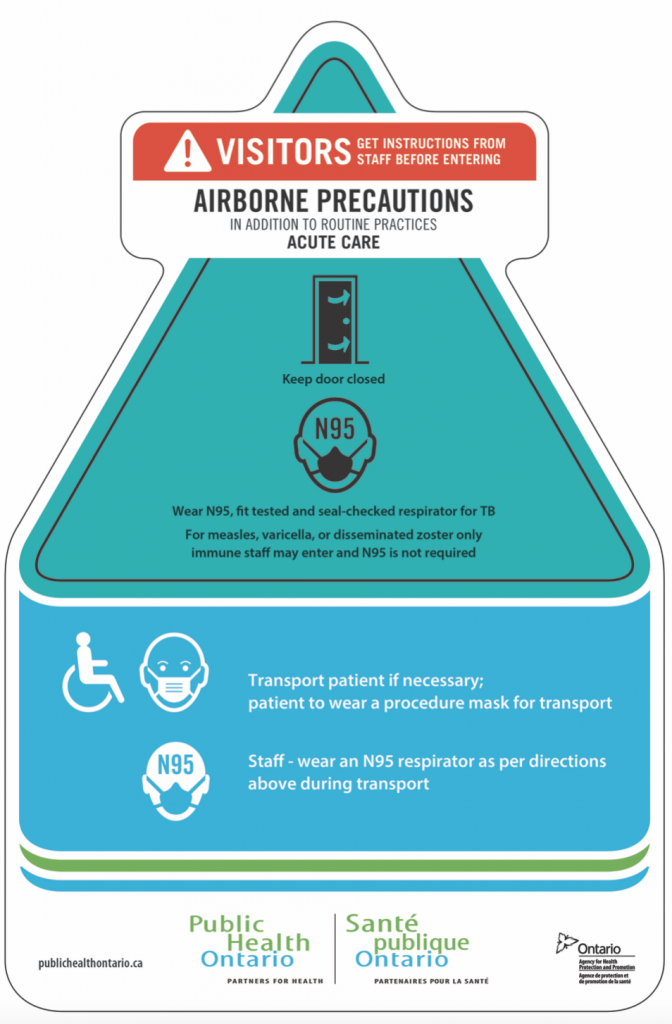
. VZV however can also be transmitted via aerosols from patients with disseminated skin lesions of varicella or herpes zoster HZ. If you are immune to varicella or measles you do not need to wear respiratory protection. Airborne Precautions Use Airborne Precautions in addition to Standard Precautions for patients known or suspected to be infected with microorganisms transmitted by airborne droplet nuclei small-particle residue -5 µm or smaller in size- of evaporated droplets containing microorganisms that remain suspended in the air and that can be dispersed widely.
Tuberculosis active cases Measles. Airborne precautions are used to help prevent the spread of pathogens that can remain suspended and infectious in the air for long periods of time. Pulmonary tuberculosis chickenpox measles.
A special note to be made is regarding COVID-19 the 21st-century pandemic which is thought to spread through airborne routes among other routes. Refer to 33 Airborne transmission for a description of airborne transmission. Airborne precautions should be continued for the handling of a patient with infectious respiratory tuberculosis measles or varicella until appropriate time has elapsed to.
Patients should stay in their rooms as much as possible while these precautions are in place. Herpes simplex virus HSV and varicella zoster virus VZV are usually spread via droplets or contact which are preventable with good hygienic practices and droplet precautions. Diseases requiring airborne precautions include but are not limited to.
Standard precautions contact precautions and airborne precautions with eye protection goggles or a face shield should be followed during the autopsy. If you are susceptible ie non-immune or unaware of your status report to your supervisor or nurses station. Stop following these precautions only when that illness has been treated or ruled out and the room has been cleaned.
Further treatment depends on your specific illness. Examples of illnesses that require airborne precautions are tuberculosis measles and chickenpox. Use Airborne Precautions for patients known or suspected to be infected with pathogens transmitted by the airborne route eg tuberculosis measles chickenpox disseminated herpes zoster.
TB Measles Varicella Disseminated Zoster SARS. Put a mask on the patient. PPE is single use.
Contact transmission direct or indirect eg. Airborne diseases Diseases caused by pathogens that small enough to be discharged from an infected person in a form of tiny drops called aerosols The pathogen remains suspended in air dust particles or respiratory and water droplets that are. You should utilize airborne precautions when a resident has a known or suspected illness such as but not limited to.
Preventing airborne transmission requires personal respiratory protection and special ventilation and air handling. You should utilize airborne precautions when a resident has a known or suspected illness such as but not limited to. Airborne Precautions Note gowns should be fluid resistant if expected or potential for working withbeing exposed to body fluids.
Influenza pertussis whooping cough rubella. Airborne precautions are used to prevent the spread of germs through the air or dust. Control and Prevention of Influenza Viruses.
Airborne precautions using N-95 masks and negative airflow rooms should be followed during aerosol-generating procedures such as bronchoscopy intubation cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR open airway suctioning and sputum induction. Generating procedures are being performed. Airborne Precautions are required for patients diagnosed with or suspected of having an infectious microorganism transmitted by the airborne route.
Focus on precautions required for immunized and non-immunized staff in relation to common airborne organisms and the differences between them. Viral gastroenteritis Clostridium difficile MRSA scabies. Coronavirus Disease 2019 COVID-19 This is a non-exhaustive list that only encompasses some of the common diseases that have been implicated in airborne transmission.
A respirator is not necessary for immunized individuals but is required for non-immunized workers who provide care. Airborne Precautions are followed in addition to Routine Practices. For Varicella chickenpox disseminated zoster or measles rubeola.
See Guidelines for Isolation Precautions for complete details. Many of the following procedures are. If exposure to bodily fluids from splashes or copious drainage is a high potential shoe covers are also to be used.
Perform Hand Hygiene HH then proceed with donning prior to entering patient. TBPs should be tailored to the particular infectious agent involved and the mode of transmission. Measles Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome SARS Varicella chickenpox and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Airborne precautions should be used for handling deceased bodies and preparing bodies for autopsy or transfer to mortuary services. Wear gloves and a gown when in contact with the individual surfaces or objects within their environment. The germs can remain in air or dust for a long.
For patients with the following various diseases list the necessary precautions. Airborne precautions are used in addition to routine practices for clients who are known to have or are suspected of having an illness that is transmitted by small droplet nuclei that may stay suspended in the air and be inhaled by others. Tuberculosis active cases Measles.
Airborne precautions should be employed in addition to standard precautions when caring for patients who are known or suspected to be infected with a microorganism that. Use contact precautions in addition to standard precautions when in contact with individuals known or suspected of having diseases spread by direct or indirect contact examples include norovirus rotavirus draining abscesses and head lice. Only healthcare providers immunized to the organism in question should enter a room where airborne precautions are in place for varicella or measles.
Airborne precautions are used to help prevent the spread of pathogens that can remain suspended and infectious in the air for long periods of time. They may need to wear a mask when they leave their rooms.

Transmission Based Precautions Wikiwand

Airborne Precautions Introduction To Infection Prevention And Control Practices For The Interprofessional Learner
![]()
Standard And Transmission Based Precautions And Signage Australian Commission On Safety And Quality In Health Care

Airborne Nursing Notes Nursing Mnemonics Basic Life Support

Infection Control And Preventions Ppt Download
![]()
Standard And Transmission Based Precautions And Signage Australian Commission On Safety And Quality In Health Care

Transmission Based Precautions Pha Infection Control

Standard Precautions Personal Protective Equipment Aplmed Academy

Transmission Based Precautions Wikiwand

Gnur 238 Contact Airborne Droplet Precautions Protective Isolation Flashcards Quizlet

Additional Precautions Signage And Lanyard Cards Public Health Ontario
![]()
Standard And Transmission Based Precautions And Signage Australian Commission On Safety And Quality In Health Care



Comments
Post a Comment